Many people look at the cloud as a way of reducing costs (no capital expenses, no real estate, no hardware management, etc.) While the cloud does offer real advantages when it comes to cost reduction, the real game-changers in the cloud are how expenditures are used and the agility the Cloud imparts to one’s business. In fact, it is this agility that is the cloud’s most important attribute.
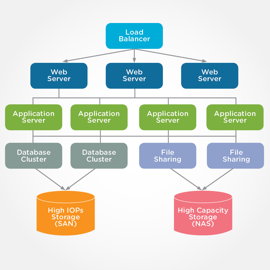
Today, most enterprise applications are accessed by users via web interfaces, and therefore are termed web applications. The recipe for these applications consists of multiple layers of interconnected servers. A typical web application architecture diagram is shown below:
The more concurrent users there are, or the more sophisticated the computation the application needs to perform, the more servers need to be deployed horizontally.
For simplicity, we did not include in this diagram disaster recovery, backup and other utility servers that are almost uniformly needed alongside any critical application.
To set up this type of web application requires acquiring multiple hardware servers, installing different operating systems and software on each of the servers, utilizing different types of storage (depending on application need), and interconnecting all these elements to one another.
In a traditional data center, setting up this type of configuration usually required weeks, perhaps months, until all components were purchased, delivered, set up and interconnected. Businesses needed to predict the amount of hardware required when placing orders, months before deployment. Furthermore, as infrastructure size needed to be anticipated with respect to the highest expected load, much of the infrastructure remained unused during standard operations and consequently was used inefficiently.
What would happen if this configuration process and period of weeks and months were reduced to minutes, or even seconds, and deployment across a horizontal scale could grow and shrink constantly and inexhaustibly according to need?
The cloud introduces this form of “Agility,” a dexterity that allows businesses an entire new approach to application deployment. Agility allows companies to quickly react to changing market needs, adjusting economies, expansion, contraction, competition and new opportunities by creating and testing more applications, onboarding more customers, and analyzing more data like never before.
More and more businesses are deploying applications on demand in the cloud for this very reason. AWS Cloud Formation and Rightscale are examples of tools that allow one to automate all steps of deploying a complex set of applications, allowing efficient provisioning and management of growing and shrinking server needs. On the cloud storage side, solutions such as our own Virtual Private Storage Arrays (VPSA™) provide agile, Enterprise-class cloud storage environments for demanding, high-performance applications that require more than basic cloud storage.
The technology is here, and the cloud’s practicality of using infrastructure more efficiently is not only a strategy for cost savings, it’s a strategy for new models and processes of an Agile Business. The ability to deploy applications more quickly, for either external or internal consumption, substantially improves the bottom line and competitive position of business of all types and sizes. Agile businesses can respond more quickly to market needs, adapt to changes, provide better service, rapidly test new products, expand geographically and/or analyze data faster; a clear advantage over competitors who have not taken advantage of the cloud’s true potential.
Cloud deployment allows businesses to move their time and resources from maintenance and infrastructure operations costs to getting technology to support and advance new processes. Businesses who think only about cost savings are missing the point. It’s not just about saving money, it’s about how to use money far, far better.
The author is CEO and Co-founder of Zadara Storage, a cloud storage startup that helps businesses become agile by providing an environment for running existing and new applications in the cloud.